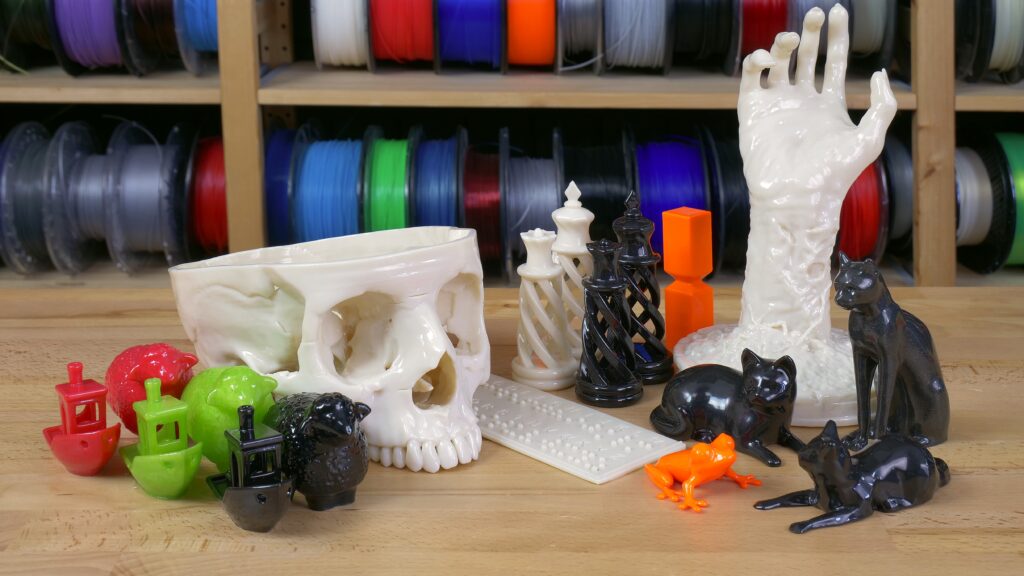
FFF 3D printers like the Original Prusa i3 MK3S enable you to print fascinating models with a very good level of accuracy. Yet sometimes it’s not enough. There are things that require a perfectly smooth and shiny surface – either for aesthetic or functional reasons. With SLA 3D printers, it’s no difficult job. But what about FFF 3D prints? Layer lines are usually quite prominent. Smoothing them out can be accomplished only by proper postprocessing. You might have heard of it, or tried it on your own already – like smoothing ASA/ABS 3D prints with acetone vapors. We still receive a lot of questions about how to make various materials smooth, though. So let us walk you through our instructions on how to make your model perfectly smooth and glossy.
Safety first:
First, we need to remind you that in all cases of chemical smoothing we’ll work with flammable organic dissolvents and/or their fumes. Please follow the recommended safety precautions to protect yourselves and the people around you. Remember that you work with these chemicals at your own risk. Do everything necessary to avoid direct contact with and inhalation of chemicals. Always work in well-ventilated areas, as far as possible from flammable objects and use protective equipment such as gloves and face protection (protective shield or protective glasses). Acetone vapors tend to be very prominent and may cause respiratory issues.
How to choose the right material
When chemical smoothing is mentioned, many users will probably remember ABS or ASA filaments as materials that can be smoothed easily. This is why we will pay attention mostly to these materials. However, these types of filament are not the only ones which can be smoothed to a certain level. Every material has its own dissolvent (you can find it in chemistry tables) that will smoothen the material sooner or later. However, not every process is recommended, because many dissolvents are usually hazardous materials that are unavailable to a vast majority of people (e.g. chloroform, dichloromethane, etc.). Moreover, dissolving some filaments takes way too long, which makes them impractical for this type of postprocessing. Let’s evaluate several basic combinations of filaments and dissolvents that are often recommended among makers and see what are their advantages and disadvantages.
ABS and ASA
By far, the most suitable materials for smoothing are ABS and ASA in combination with acetone. You should be able to buy acetone at your local drugstore or hardware store and use it in your home workroom. Prusament ASA, in particular, can be smoothed out easily. And using the right method, you’ll get a nice smooth and shiny surface in no time. We will pay more attention to ABS and ASA in the following chapters.
PVB
Another very popular material is PVB (PolyVinyl Butyral), because it’s also easy to use (like PLA), it’s not prone to warping and it can be smoothed with isopropyl alcohol (IPA). However, if you use IPA vapors for smoothing (as you would with ABS/acetone), the process might take up to several hours. To speed it up, IPA should be applied directly onto the surface of your 3D prints. It’s better to disperse it just like the Polymaker Polysher and Zortrax Apoller do it.
HIPS
HIPS, aka high-impact polystyrene is generally used as a support material for ABS and ASA prints. It can be dissolved with d-lemonene. The best way is to wash the model for 10-20s in lemonene and let it dry (it might take several hours or even days). Curiously, the model will always smell like orange peels as a result of being washed in d-lemonene. We’ve tested that some HIPS can also be smoothed with acetone (the best way is to use acetone fumes).
HIPS smoothed with acetone (left) and D-lemonene (right)
PLA
Smoothing PLA is a little bit more challenging. Various internet discussions offer many tips and tricks on how to do it. And apparently, there is quite a lot of people who did it successfully with some of the following methods. The most frequent piece of advice is to use chloroform. However, it is a dangerous chemical that can be obtained only with special permission that most people won’t get. Even we were unable to get our hands on this chemical, so at this point, we can’t confirm whether it works or not.
Another option is to use NaOH (Sodium hydroxide aka lye). We can’t recommend this method either, especially if you intend to do it at home. It’s a dangerous substance and usually, instead of smoothing your print, it will most likely disintegrate the object into small fragments. There is a small chance of getting a better result with various concentrations but we cannot confirm that. More testing in laboratory conditions would be required.
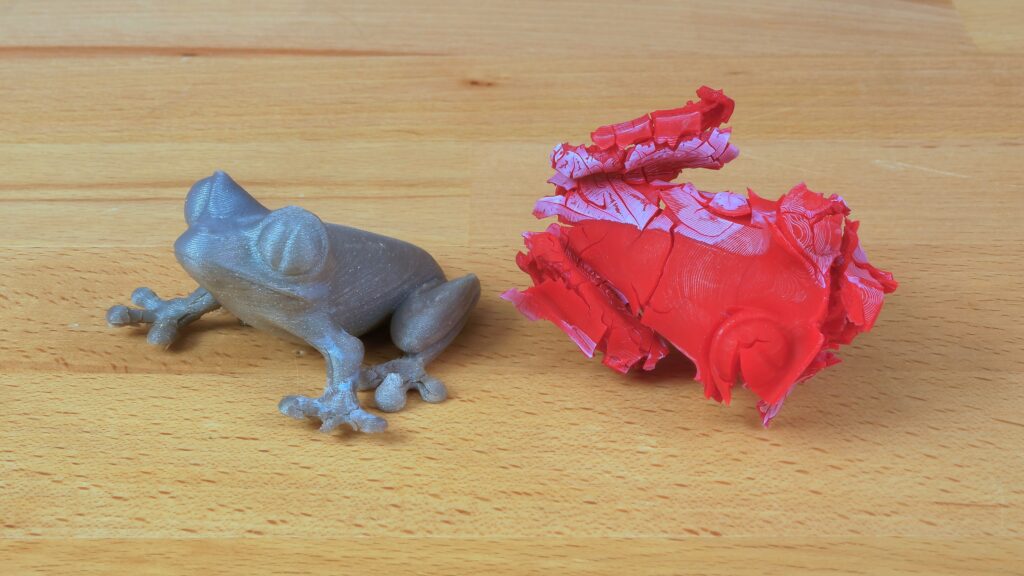
The third piece of advice is using acetone. Our tests confirmed that all colors of Prusament PLA can be glued together perfectly with acetone – it works as a superglue. However, our attempts at dissolving PLA with acetone can be hardly called successful. We printed samples of almost every Prusament PLA and exposed them to acetone vapors. After several hours of exposition, they got a little bit softer, but not even close to being smooth. Then, we’ve tried to apply acetone onto the model’s surface directly using a brush, again with no noteworthy result. Finally, we’ve submerged the models in an acetone bath, which caused partial bleaching of several filaments and total destruction of all models. A short bath won’t cause any particular damage, but after a few hours (or even days), the model will crack not only between layers but also in other directions (it’s caused probably by an effect called “solvent crazing”). It’s interesting that the layers remained visible in every case, no matter what happened to the rest of the mode.
PLA treefrog bathed in acetone for 3 hours and 48 hours
PETG
You can smooth out PETG, too. The best way is to use dichloromethane. The main advantage of PETG smoothing is the fact that the chemical can be applied with a brush easily – it does not leave marks on the surface and the prints won’t twist afterward (like ABS or ASA). But there’s a catch: dichloromethane is a dangerous dissolvent just as chloroform and can be bought only with special permission. These chemicals should be used only by experienced users with proper protection.
Dissolvent application
Most of the dissolvents can be applied in several ways but we’ve tried them and confirmed that one solution stands above the rest: the best way to make your print smooth is to expose it to dissolvent fumes. Applying the dissolvent with a brush will most likely consume a lot of the chosen chemical and the surface will never be perfectly smooth and shiny. Plus you risk leaving white marks on the surface. The model could also start to twist and warp. Sinking a 3D print directly into, for example, an acetone bath is also not a good idea. It introduces various issues with the handling of the object – you will most likely touch it while removing it from the bath and damage the softened surface. Plus, the dissolvent can leak inside your model and cause even more damage. Not only that, but it’s usually difficult to estimate the correct submersion time, so in the end, you will more likely spoil the bath with dissolved plastic. ABS/ASA-based objects treated this way tend to twist a lot.
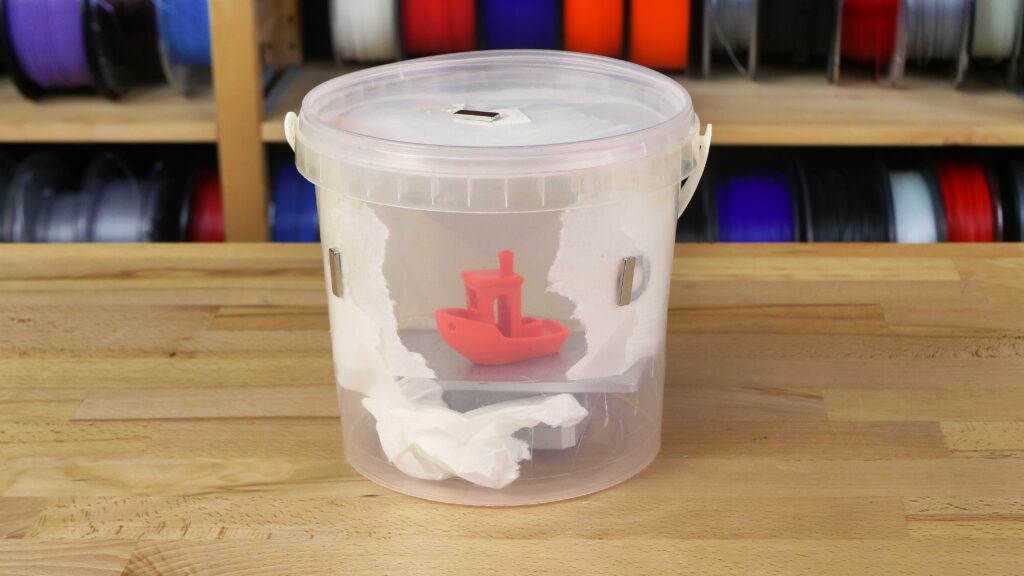
Smoothing box construction
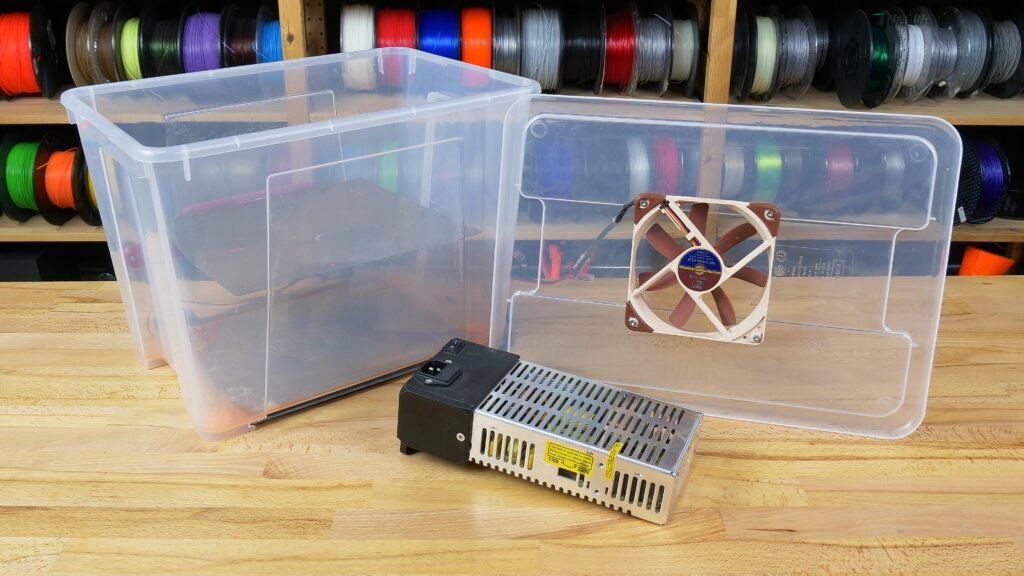
At this point, we have decided that we need to use dissolvent vapors to smooth out our prints. To do this, we’ll need to build a proper box to succeed. It should have several basic parameters:
First, let’s decide which chemicals we plan to use and choose a suitable material for the box. You shouldn’t use a box made of ABS for acetone smoothing or PETG box for dichloromethane smoothing, because they would quickly dissolve. Since ASA/acetone is the most used combination, we chose a transparent PP (polypropylene) storage box available at IKEA. It’s good to have several boxes of different sizes for various models to save acetone and make the process a little bit faster.
Examples of smoothing boxes: An elevated platform (old and damaged spring sheet works fine) is necessary Electronics are optional and should be used by experienced users only!
The most common and the safest process is placing napkins or pieces of toilet paper soaked with acetone under and around the model. This works well for tiny models. However, with larger models, this becomes much more challenging, because the smoothing effect may not be consistent across the entire surface – e.g. the lower part may be smoother than the top part. Of course, there are some methods that can make this work even with larger models. First, the most recommended and the safest method is getting a professional smoothing station, such as Polymaker Polysher or Zortrax apoller. These machines work at low temperatures, disperse the dissolvent equally and create a nice glossy look. The downside of smoothing stations is their high price.
There is one more (and cheap) method how to make every model smooth evenly – and that is warming the acetone. But be aware that this method is dangerous and we cannot stress this more – if you decide to heat acetone, you are doing it at your own risk. Do it as far as possible from anything flamable, wear protective equipment (face shield, gloves etc.) and always check the box (stay in a distance and always watch it). Working in a safe environment is absolutely essential – we can’t stress that enough. If you are not sure about it, use the cold method or buy a professional smoothing station. Better safe than sorry!
Now, if you aren’t discouraged by our safety warnings, let’s see the list of recommended hardware. As we said, we’re going to heat up the acetone bath. Its fumes will increase in volume and if there would be a source of ignition in the sealed box, it could cause an explosion. Please, keep in mind that the box must not be perfectly sealed to prevent pressure build-up inside. We recommend using a light plastic plate with no locks (just lying on top of the box) and making a couple of tiny holes in the lid to help acetone fumes escape. Under no circumstances a box with rubber isolation and any type of locks should be used!
Place a metal plate inside the box and make sure it’s at least a few centimeters (1-2 inches) above the bottom. This will serve as a baseplate for smoothened models. The platform must be raised to prevent direct contact of models with acetone. We found an old printer steel sheet to be the best smoothing pad. We can work with it easily, without touching the models.
Another thing your box might need is a fan. It is an optional part, but it will truly improve the effectivity due to improved air circulation. Without a fan, your models might get too soft at the bottom, but visible layers on the top might remain. The ventilator should be placed at the underside of the lid, so the airflow is directed right onto the models. Again, safety first: The fan should be working perfectly if you decide to put it inside of the box. Damaged electronics can cause spark and ignite the fumes. If you are unsure about the quality of the fan, do not use it!
The second optional part is a heated pad. Heating will saturate the air inside with acetone fumes better and accelerate the whole process. If you don’t feel like constructing a heated pad, you can also place the box onto a warm (not hot!) surface (a sun-heated pavement, printer heatbed, etc.). However, enthusiasts can build their own integrated heating. Before you try to add a heated element, remember that the heating must be placed outside of the box! It is not a good idea to insert a heater inside the acetone bath!
We are repeating ourselves, but a reminder doesn’t hurt: be careful with flammable organic dissolvents used in the smoothing process! Do not leave the box unattended when the process is running! We are using a smoothing box with a Noctua fan and a heatbed from the MK3S regularly for many months and we experienced no issues. However, we still recommend to exercise appropriate caution!
Amount of acetone, time and temperature
It’s time to test the smoothing box! It might take some time before you find the perfect balance of exposure time, temperature, and amount of acetone. For our setup, the best temperature of heatbed is approx. 80°C, with approximately 5 mm of acetone at the bottom and 20 minutes of exposure. However, keep in mind that you need to check your print regularly: If you expose it for too long, it can deform irreversibly.
The model can stay quite soft for several hours after smoothing. Remember that before removing it from the box. You can easily damage the softened surface merely by touching it. It might feel solid if you touch it gently, but don’t be mistaken. It’s better to leave the model on the pad and remove it from the box with it. Take the pad with your models and place it into a dry clean box and leave the models to recover for at least several hours (or even a whole day). This way, you will ensure that no fingerprints are visible on the surface and no dust particles are caught on it.
Don’t be surprised if you find out that the model smells like acetone a few days after. It takes some time for the chemical to evaporate completely.
Choosing the suitable models
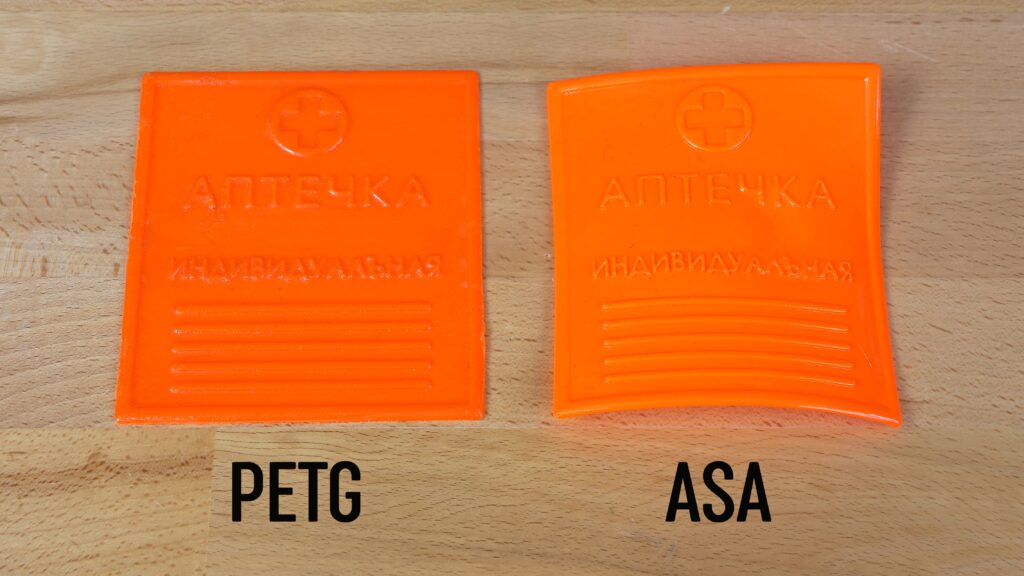
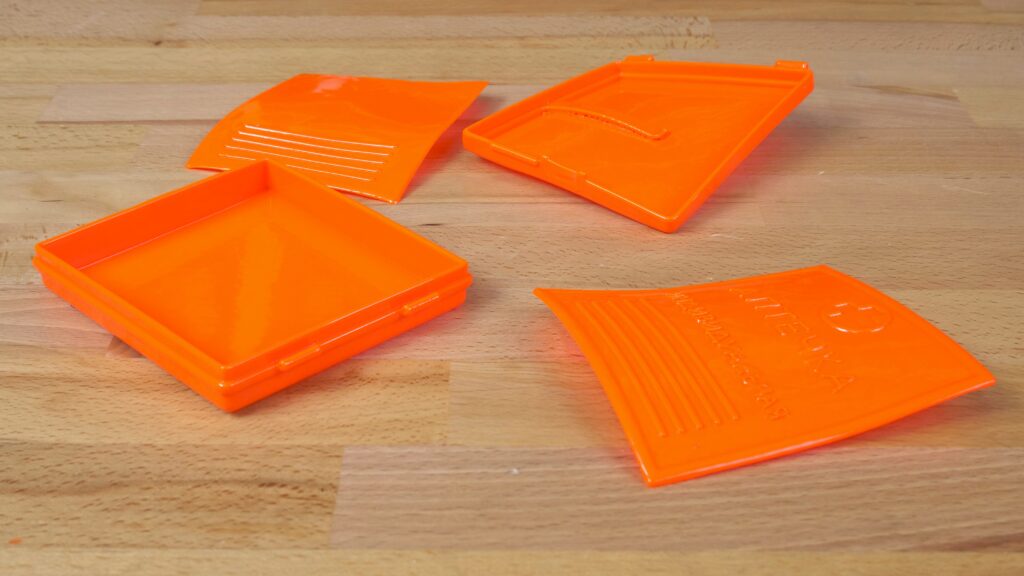
Not every model is suitable for acetone smoothing. Tiny and complex structures are usually not good since they usually lose their details and/or start to deform. This also applies to large and flat models: for example, this medkit will sooner or later deform after being smoothed in acetone vapors. Plus, ASA and ABS tend to warp during the printing process if you don’t have your printer inside an enclosure.
Tip: If you don’t have any enclosure, set the skirt in PrusaSlicer (Print settings/skirt and brim) to the highest possible number of layers (9999). This will help to create a microclimate and reduce warping a lot. The layer height is also a huge factor. The lower your layer height is, the better the smoothing process gets. Try to experiment with variable layer height to achieve the best results.
It’s good to use an enclosure for ASA prints to reduce warping.
Thin parts tend to twist after smoothing and can become unusable.
Functional (mechanical) parts are not suitable for acetone smoothing. The process can change their dimensions and shapes (especially sharp edges) and it will not improve their mechanical properties – it’s only aesthetical.
A little bit of testing
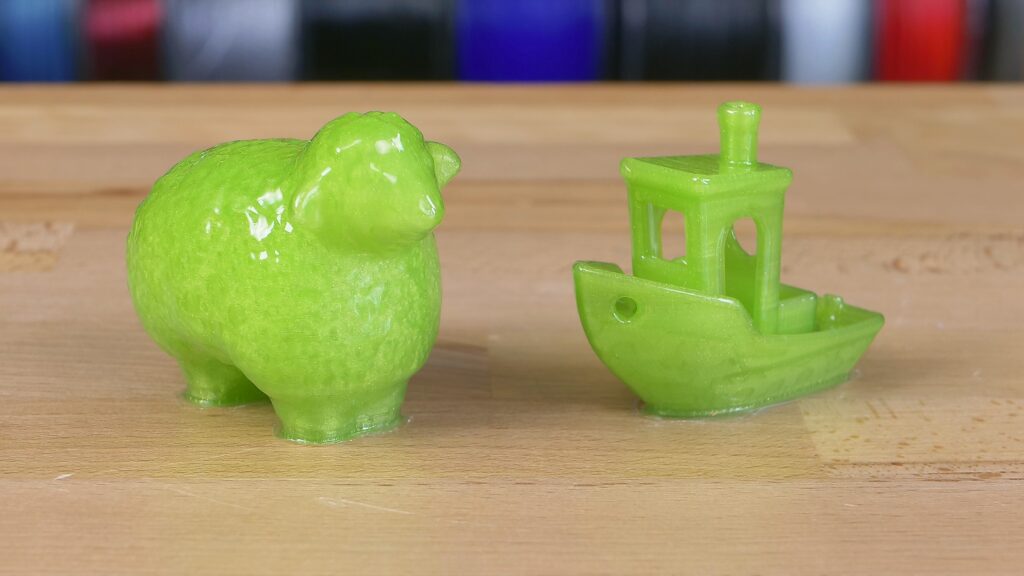
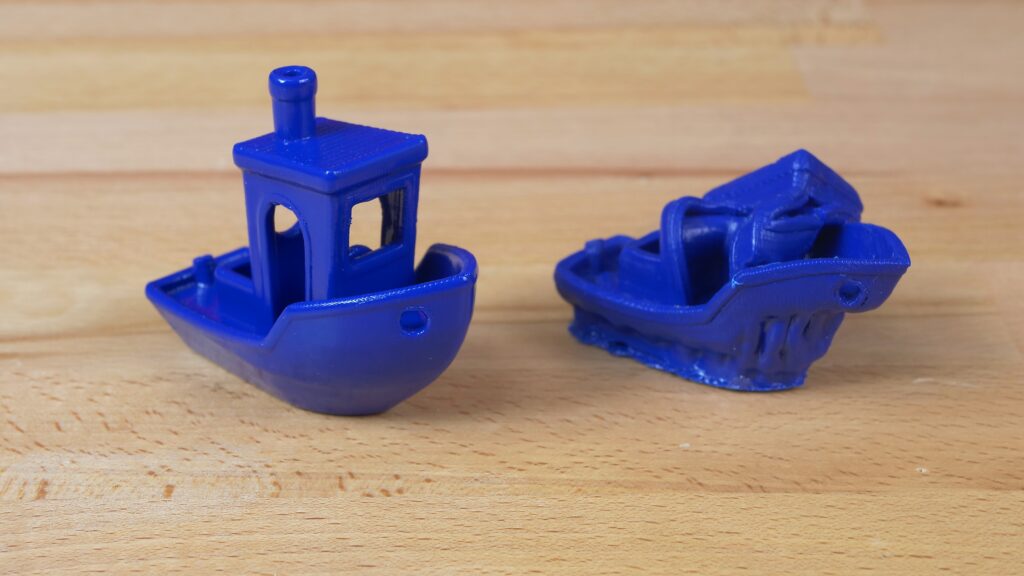
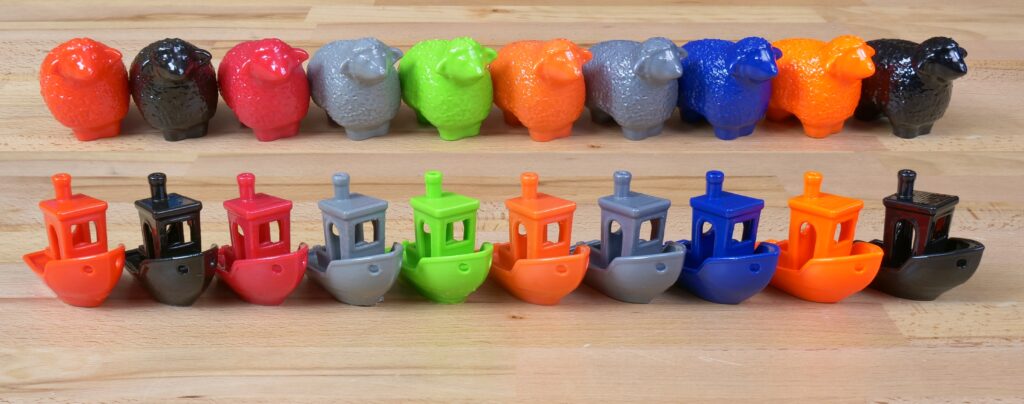
We thought that you might be interested in the comparison of various ABS and ASA filaments. We printed two sample objects (3Dbenchy and a sheep) with 10 different filaments and smoothed them out with acetone vapors. And the results differ – a lot.
Here’s our list of tested brands and materials: Fiberology ABS, Filament PM ASA, ABS, ABS-T, Gembird ABS, Hatchbox ABS, Nebula ABS 702, Prusament ASA, Spectrum ASA 275
The easiest (fastest) to smooth was our Prusament ASA Prusa Orange. For this filament, 15-20 minutes of exposure was more than enough and the result was a nice glossy surface. Most of the other filaments could be smoothed after a little longer time (20-40 minutes) with a few exceptions: ABS-T by Filament PM (green) and Spectrum ABS 275 (blue) had clearly visible layers even after one hour of exposure. With a longer time these models started to deform, but the layers remained visible. Similarly, the layers were visible on grey ASA by Filament PM (fourth from the right). However, what was interesting, was the fact that the perceived layer visibility was caused only by the pigment – the surface was in fact as clear as a mirror.
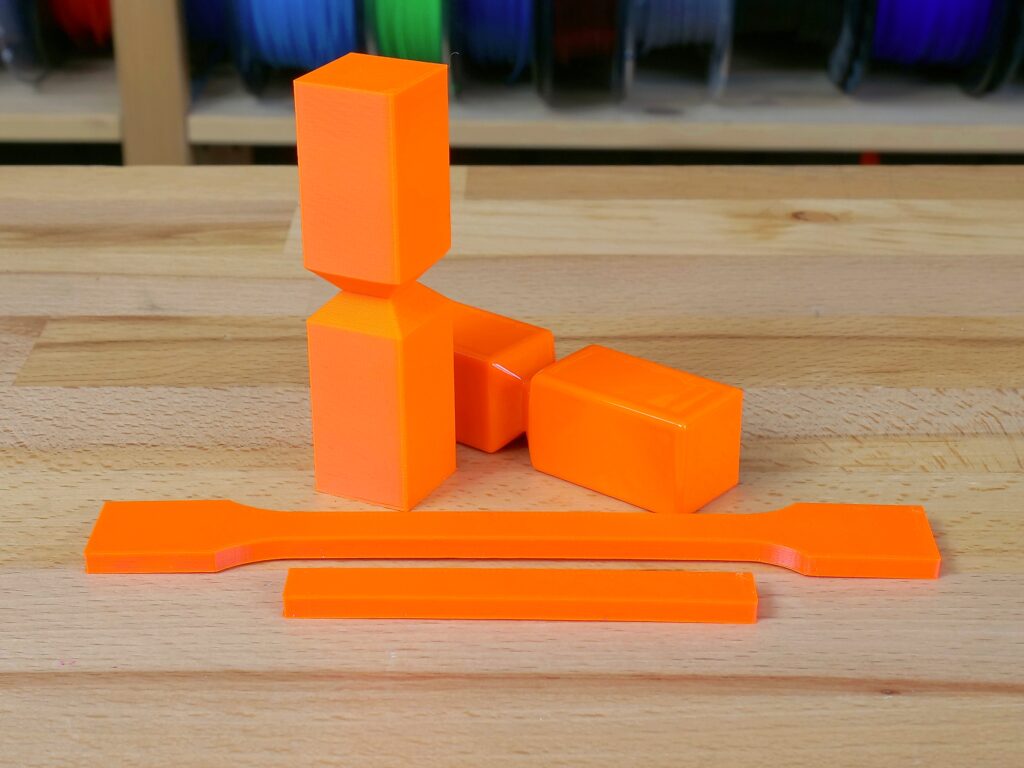
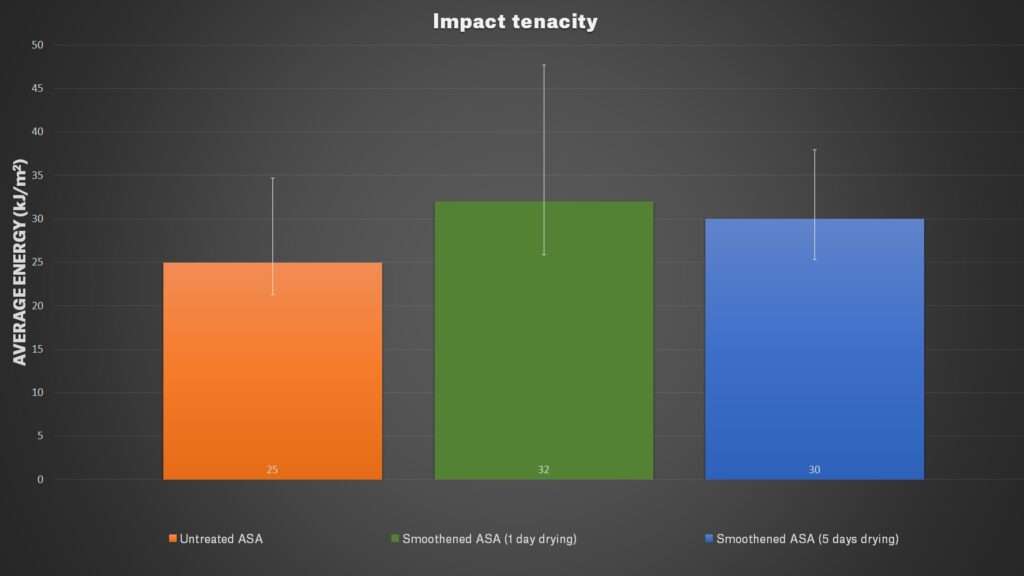
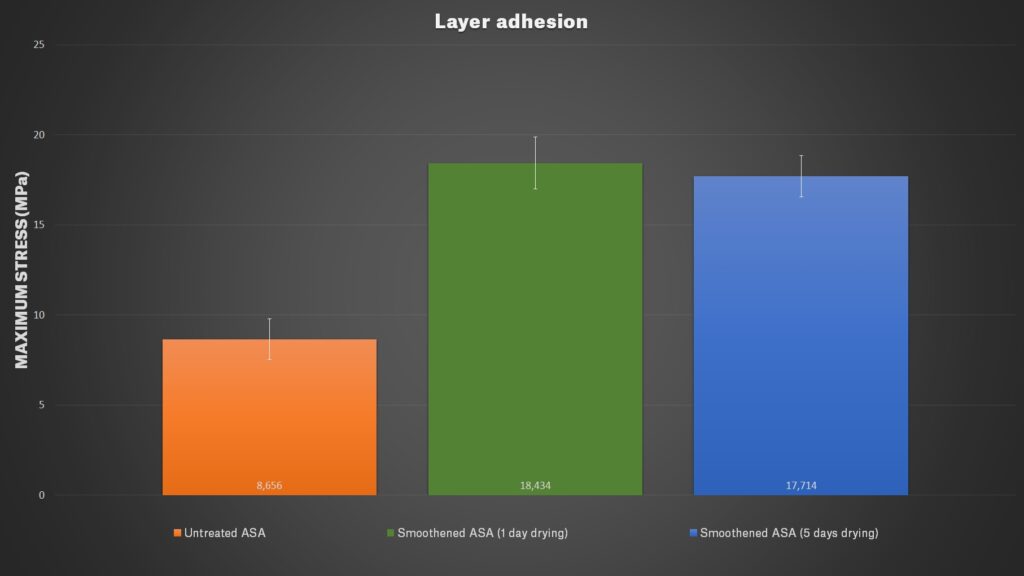
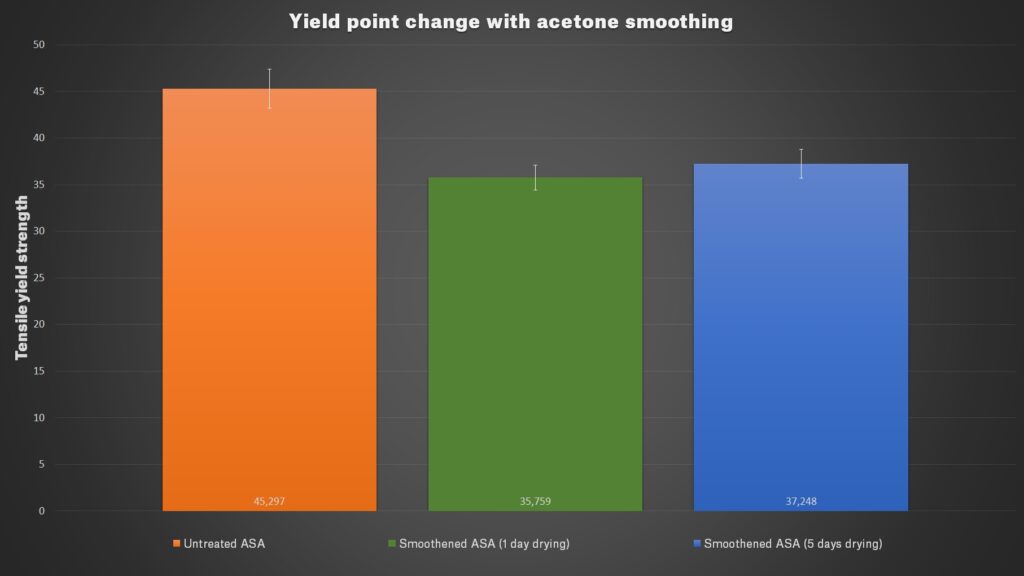
Finally, we tested a few physical properties of our Prusament ASA Orange. We were interested in the difference between untreated and smoothed objects. We printed 60 test objects for the Charpy pendulum test, 30 sample objects for traction test, and 15 objects for layer adhesion test. Two-thirds of all models were treated with acetone for 30 minutes. The smoothened models were split into two batches, one was dried for one day and second for five days. Then we tested it the same way we did it in our annealing article.
The results showed us that smoothened models have slightly better tenacity than the untreated ones, plus they have more than twice better layer adhesion. On the other hand when testing tensile strength, the force at which material tears were a little bit lower for smoothened parts.
As you can see, acetone smoothing is not rocket science. With several simple gadgets, you can make it work even in your garage or workshop without any difficulties. So go ahead and give your models the professional look they deserve 🙂 Just don’t forget about safety! Always use protective equipment, work in well-ventilated spaces, and don’t leave the smoothing box unattended. We’re really curious to see your creations, so don’t forget to share the photos and your own tips and tricks on smoothing. And as always – Happy printing!















It would be super interesting a how to guide to build the heated box.
https://media.prusaprinters.org/media/prints/405/stls/2713_8fe4d7bb-5071-422a-9b2d-806021242d78/14_014_prusament_simple.stl
Whoops, wrong post. my bad
What a good article. It is unfortunate that I did not find her before. The information I need is completely outlined here. My chemistry task was to write an essay on a similar topic. I was looking for a source of information, but could not find it. But I found a site https://pickthewriter.com/ on which I read the reviews and chose a written service that wrote me an essay. But if I saw this article earlier, I would use this information and complete the task myself. I’ll copy myself the text, maybe I’ll use it for the next essay. Thanks to the author.
Hi
Thanks for the nice summary.
You may also want to take a look at 1,3-dioxolane which works really well to smooth PLA. This solvent is found in paint stripping product, for example in Montana Spray cans. More details here: https://www.instructables.com/id/Smoothing-3d-Print-PLA-With-13-dioxolane/
Have a great day,
Matt
I can say for sure from myself that now there are a lot of different things to write and often there are no ideas. This is already more than familiar to me. That’s why I can say purely from myself that of course you need to understand that an idea may never work. That’s why it’s easier to refer to professional writers who can quickly write any project https://writemyessay4me.org/capstone-project . I have addressed them more than once and I am very happy about it. Because it is necessary to apply to them too, I think it will not be superfluous. Good luck and success! I hope that I helped!
When ordering an essay, I was most worried about the quality of work. So that the teacher did not suspect anything, but it was senseless to worry, the guys of https://expertpaperwriter.com/edubirdie-com-review/ have long shown themselves from a good side.
When ordering an essay, I was most worried about the quality of work. So that the teacher did not suspect anything, but it was senseless to worry, the guys of https://www.google.com/ have long shown themselves from a good side.
Is it a bad idea to use a heating plate like with induction, some metal support to get the heat and just a glass Jar with a ventilator mounted on the lid?
A great article, thank you!
This is Couponsva, a professional blogger I enjoy writing on multiple callings with a firm grip on specialty include digital marketing, affiliate marketing, entertainment, and e-commerce blogs.
Thank you!
completely resolved my question when I read this post, thanks to the author for the very detailed description. I wrote my review on the Commercial Cleaning Perth
https://www.affordable-papers.net/
in addition to chemical smoothing you can use hot air. I have a hot air desoldering tool with variable temp. with the proper tip you can melt the outer surface without doing any viewable damage. Works well on pla.
Hello to the whole community 😀
I am looking for a cheap motherboard to make the polishing box.
Just to control my old mk2s heated bed is the fan
Can someone please me
I had a bug or message too long 😅
If anyone has a reference in mind, I’m all ears.
Thanks in advance to the community 😀
Thanks for the informative article.
Question: it is stated: that smoothing does not improve mechanical properties. Yet the tests show a remarkable increase in impact tenacity and layer adhesion. Could you please explain?
Suggestion:
As a safe way to heat the acetone a pan of hot water comes to mind. No heat source around that could give ignition, and temperature is easily controllable: just add more hot/cold water.